Knee bursitis is a painful condition that occurs when the bursae—small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles around your knee—become inflamed. This condition can significantly limit your ability to perform daily activities, from walking to bending your knee. While rest and over-the-counter medications can help reduce the initial inflammation, long-term management often requires a more structured approach. Physiotherapy is a highly effective treatment option for knee bursitis, offering various techniques to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and prevent recurrence. In this blog post, we will explore seven ways physiotherapy can help treat knee bursitis.
1. Pain Management for Knee bursitis
Pain is the most common and distressing symptom of knee bursitis. Physiotherapists employ several strategies to manage pain effectively, allowing patients to engage in their daily activities with minimal discomfort.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice to the affected area helps reduce inflammation and numb the pain. Physiotherapists often recommend using ice packs for 15-20 minutes several times a day during the acute phase of bursitis.
- Ultrasound Therapy: This treatment uses sound waves to generate heat deep within the tissues, which can help reduce pain and promote healing. Ultrasound therapy is particularly beneficial for chronic bursitis where inflammation persists.
- Electrical Stimulation: Techniques like Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) use low-voltage electrical currents to disrupt pain signals, providing relief from knee pain.
By managing pain effectively, physiotherapy helps patients remain active, which is crucial for long-term recovery.
2. Reducing Inflammation

Inflammation is a key factor in the development and persistence of knee bursitis. Physiotherapists employ various techniques to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Compression: Applying compression bandages or wraps can help reduce swelling by limiting the amount of fluid that accumulates in the knee joint. This is often combined with rest and elevation to maximize the anti-inflammatory effects.
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage: This specialized massage technique encourages the movement of lymphatic fluid, reducing swelling and inflammation. It’s particularly effective in chronic cases where fluid buildup is significant.
- Anti-inflammatory Exercises: Gentle, low-impact exercises prescribed by a physiotherapist can help reduce inflammation by promoting circulation without exacerbating the condition.
Reducing inflammation not only alleviates pain but also prevents further damage to the knee structures.
3. Improving Mobility
Knee bursitis often results in stiffness and a reduced range of motion. Physiotherapy focuses on restoring mobility through a combination of stretching and strengthening exercises.
- Range of Motion Exercises: These exercises help to gently stretch the muscles and tendons around the knee, improving flexibility and reducing stiffness. Common exercises include knee bends, hamstring stretches, and calf stretches.
- Joint Mobilization: Physiotherapists may use hands-on techniques to gently mobilize the knee joint, improving its range of motion and reducing stiffness. This can be particularly beneficial in cases where the knee joint has become significantly restricted.
- Proprioceptive Training: Exercises that improve proprioception (the body’s ability to sense its position in space) can enhance knee stability and function, making everyday movements more comfortable.
By improving mobility, physiotherapy helps patients regain their independence and return to their normal activities more quickly.
4. Strengthening Muscles to recover from Knee bursitis
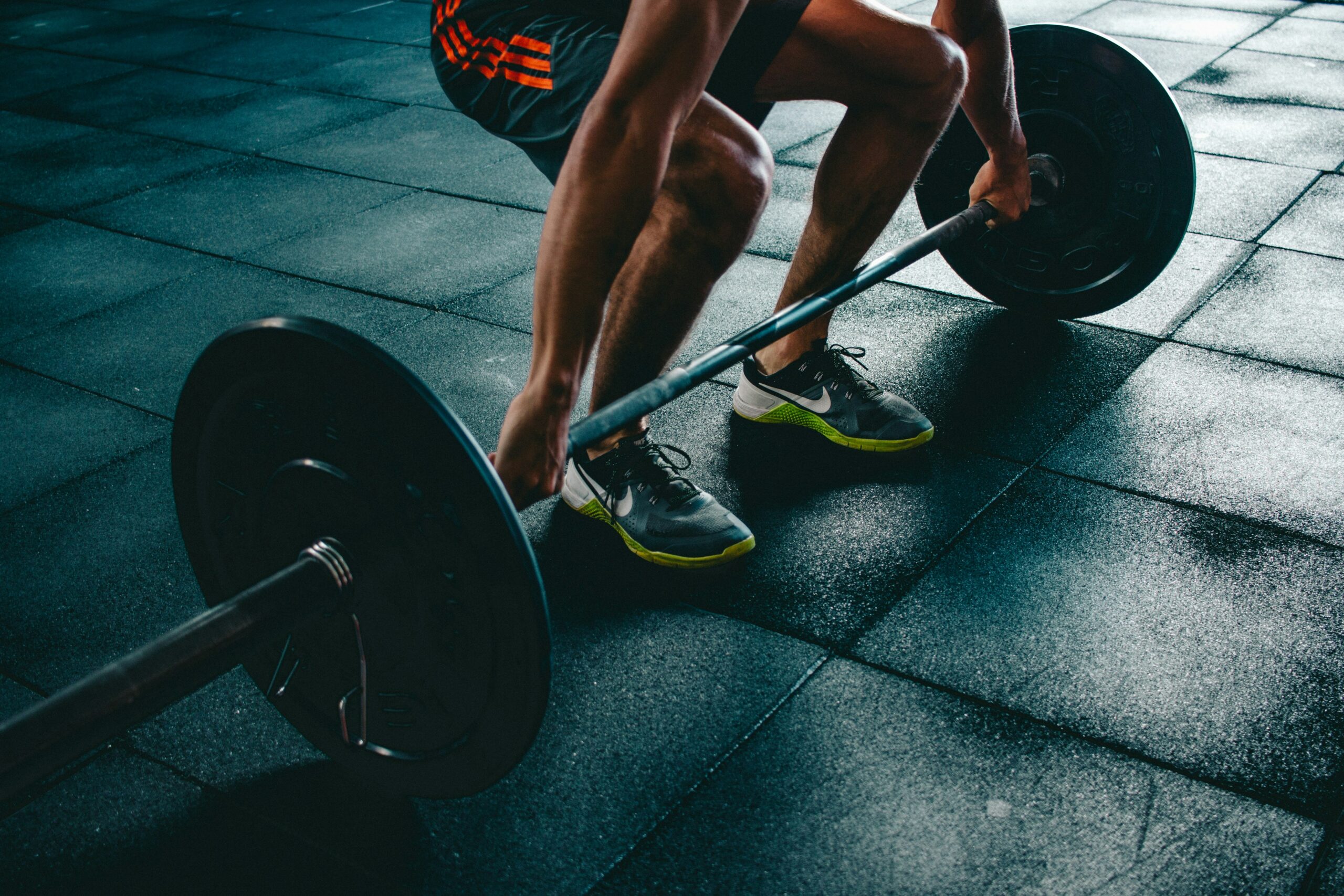

Weakness in the muscles surrounding the knee can contribute to the development and persistence of bursitis. Strengthening these muscles is a key component of physiotherapy.
- Quadriceps Strengthening: The quadriceps are the primary muscles involved in knee extension. Strengthening these muscles can help reduce the load on the knee joint and improve overall stability. Exercises like leg presses, straight leg raises, and squats (modified to avoid aggravating the bursitis) are commonly used.
- Hamstring Strengthening: The hamstrings work in opposition to the quadriceps and are crucial for knee flexion. Strengthening these muscles can balance the forces across the knee joint, reducing the risk of further injury. Hamstring curls and bridges are effective exercises for this purpose.
- Gluteal Strengthening: The gluteal muscles, particularly the gluteus medius, play a significant role in stabilizing the pelvis and knee during movement. Strengthening these muscles can reduce the stress on the knee, helping to alleviate bursitis symptoms. Exercises like clamshells and lateral leg raises are commonly prescribed.
Strengthening the muscles around the knee not only helps treat existing bursitis but also prevents future occurrences by improving knee stability and function.
5. Correcting Biomechanics
Poor biomechanics can place excessive stress on the knee joint, leading to or exacerbating bursitis. Physiotherapy aims to identify and correct these biomechanical issues.
- Gait Analysis: Physiotherapists can analyze a patient’s walking or running gait to identify any abnormalities that may be contributing to knee bursitis. Issues like overpronation, excessive heel strike, or an uneven stride can be addressed with specific interventions.
- Footwear Recommendations: Proper footwear is essential for maintaining good biomechanics. Physiotherapists can recommend shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning, or suggest orthotics to correct foot alignment issues.
- Posture Correction: Poor posture, especially during activities like running, cycling, or even sitting for long periods, can contribute to knee bursitis. Physiotherapists can provide exercises and advice to improve posture, reducing stress on the knee joint.
Correcting biomechanics not only helps treat knee bursitis but also reduces the likelihood of other injuries, promoting overall joint health.
6. Education and Self-Management
6. Education and Self-Management
Physiotherapy isn’t just about in-clinic treatments; it also involves educating patients on how to manage their condition at home and prevent future flare-ups.
- Activity Modification: Patients are often advised to modify their activities to avoid aggravating their bursitis. This might involve reducing the intensity or frequency of certain exercises, avoiding kneeling or squatting, or using assistive devices like knee pads.
- Home Exercise Program: Physiotherapists provide patients with a tailored exercise program to be performed at home. This program typically includes stretching, strengthening, and mobility exercises designed to maintain progress made during in-clinic sessions.
- Ergonomic Advice: For patients whose bursitis is related to occupational activities, physiotherapists can offer advice on how to modify their work environment to reduce strain on the knee. This might include adjusting chair height, using a footrest, or altering work tasks to reduce kneeling or squatting.
By empowering patients with the knowledge and tools to manage their condition, physiotherapy helps ensure long-term success in treating knee bursitis.
7. Preventing Recurrence
One of the main goals of physiotherapy in treating knee bursitis is to prevent the condition from recurring. This involves a combination of strengthening, education, and lifestyle changes.
- Regular Exercise: Maintaining a regular exercise routine that includes strengthening and stretching exercises can help keep the muscles around the knee strong and flexible, reducing the risk of bursitis returning.
- Weight Management: Excess body weight places additional stress on the knee joints, increasing the risk of bursitis. Physiotherapists can provide advice on weight management strategies to help reduce this risk.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments with a physiotherapist can help monitor the knee’s condition and address any early signs of bursitis before they become more serious. This proactive approach is key to preventing recurrence.
Preventing recurrence is crucial for maintaining long-term knee health and ensuring that patients can continue to engage in their preferred activities without pain.
Knee bursitis is a painful and limiting condition, but with the right approach, it can be effectively managed and treated. Physiotherapy offers a comprehensive and individualized treatment plan that addresses the root causes of bursitis, alleviates symptoms, and prevents recurrence. By focusing on pain management, reducing inflammation, improving mobility, strengthening muscles, correcting biomechanics, and providing education and self-management strategies, physiotherapy helps patients recover from knee bursitis and regain their quality of life.
If you’re struggling with knee bursitis, consider consulting a physiotherapist to develop a tailored treatment plan that meets your needs. With the right care and commitment, you can overcome knee bursitis and return to your daily activities pain-free.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of IT Band Syndrome, consider consulting a healthcare professional or physiotherapist to develop a personalized treatment plan. With the right care and attention.






