Knee ligament injuries can be a significant setback for individuals of all ages and activity levels. Whether it’s a sprained ligament or a more severe tear, these injuries can impact mobility, stability, and overall quality of life. Fortunately, with advancements in treatment and rehabilitation techniques, individuals can embark on a journey to recovery with the guidance of physiotherapy. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore knee ligament injuries, their causes, symptoms, and delve into how physiotherapy can play a pivotal role in the recovery process.

Understanding Knee Ligament Injuries:
The knee joint is stabilized by four main ligaments: the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and lateral collateral ligament (LCL). These ligaments play a crucial role in providing stability and preventing excessive movement of the knee joint. Ligament injuries can range from mild sprains, where the ligament is stretched but not torn, to severe tears that require surgical intervention.
Causes of Knee Ligament Injuries:
- Sports Activities: Knee ligament injuries are common among athletes and individuals who engage in sports activities that involve sudden stops, changes in direction, or high-impact movements. Sports such as soccer, basketball, football, skiing, and tennis carry a higher risk of knee ligament injuries due to the dynamic nature of the movements involved.
- Traumatic Events: Traumatic events, such as falls, accidents, or direct blows to the knee, can cause ligament injuries. These sudden forces can exceed the ligament’s tensile strength, leading to sprains or tears.
- Overuse or Repetitive Strain: Overuse or repetitive strain on the knee joint, particularly during activities that involve repetitive bending, twisting, or jumping, can increase the risk of ligament injuries. This is common among individuals who participate in endurance sports or activities with repetitive movements.
- Biomechanical Factors: Biomechanical factors such as muscle weakness, imbalance, or poor alignment can predispose individuals to knee ligament injuries. Weakness in the muscles surrounding the knee joint, particularly the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles, can compromise joint stability and increase the risk of injury.
Symptoms of Knee Ligament Injuries:

The symptoms of knee ligament injuries can vary depending on the severity and location of the injury, but common signs include:
- Pain, swelling, and tenderness around the knee joint
- Instability or a feeling of “giving way” in the knee
- Limited range of motion and stiffness
- Bruising or discoloration around the knee
- Audible “popping” or “snapping” sensation at the time of injury
Treatment Options for Knee Ligament Injuries:
- Conservative Management: Mild to moderate knee ligament injuries, such as sprains or partial tears, may be managed conservatively with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Bracing and Immobilization: In some cases, bracing or immobilization of the knee joint may be necessary to provide support and stability during the healing process. This helps protect the injured ligament from further stress and promotes optimal healing.
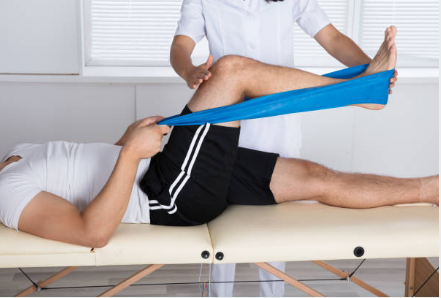
- Physical Therapy: Physiotherapy is a cornerstone of treatment for knee ligament injuries, offering a comprehensive approach to rehabilitation. Physiotherapists use a combination of techniques to reduce pain, improve range of motion, strengthen muscles, and restore function in the injured knee.
- Surgical Intervention: Severe knee ligament injuries, such as complete tears or multi-ligament injuries, may require surgical intervention to repair or reconstruct the damaged ligaments. Surgical techniques, such as ACL reconstruction or ligament repair, aim to restore stability and function to the knee joint.
How Physiotherapy Helps in Recovery:
-
- Pain Management: Physiotherapists employ various modalities, such as ice therapy, heat therapy, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation, to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in the injured knee joint.
- Range of Motion Exercises: Physiotherapists prescribe specific exercises to improve range of motion in the knee joint, helping to restore flexibility and mobility. These exercises may include gentle stretching, passive range of motion exercises, and joint mobilizations.
- Strength Training: Strengthening exercises targeting the muscles surrounding the knee joint are essential for promoting stability and preventing re-injury. Physiotherapists design personalized exercise programs that focus on strengthening the quadriceps, hamstrings, calf muscles, and hip muscles.
- Balance and Proprioception Training: Balance and proprioception training are crucial for improving neuromuscular control and reducing the risk of falls or re-injury. Physiotherapists incorporate balance exercises, proprioceptive drills, and functional activities to enhance joint stability and control.
- Functional Rehabilitation: Functional rehabilitation focuses on restoring functional activities and sports-specific movements. Physiotherapists work closely with patients to address any biomechanical issues, modify movement patterns, and gradually reintroduce sports-specific activities to ensure a safe and successful return to play.
- Education and Injury Prevention: Education plays a vital role in knee ligament injury recovery, empowering individuals to understand their injury, adhere to rehabilitation guidelines, and make informed decisions about their recovery. Physiotherapists provide guidance on injury prevention strategies, proper warm-up techniques, and appropriate equipment use to reduce the risk of future injuries.
Recovering from a knee ligament injury requires patience, dedication, and a comprehensive rehabilitation approach. Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the recovery process, helping individuals rebuild strength, stability, and confidence in their knee joint. By following a structured rehabilitation program and working closely with a physiotherapist, individuals can overcome pain and functional limitations, and return to their normal activities with renewed strength and resilience. Remember, with the right support and guidance, the journey to recovery from a knee ligament injury is within reach.






